The documentation you are viewing is for Dapr v1.8 which is an older version of Dapr. For up-to-date documentation, see the latest version.
Overview of Dapr in self-hosted mode
Overview
Dapr can be configured to run in self-hosted mode on your local developer machine or on production VMs. Each running service has a Dapr runtime process (or sidecar) which is configured to use state stores, pub/sub, binding components and the other building blocks.
Initialization
Dapr can be initialized with Docker (default) or in slim-init mode. It can also be initialized and run in offline or airgap environments. The default Docker setup provides out of the box functionality with the following containers and configuration:
- A Redis container configured to serve as the default component for both state management and publish/subscribe.
- A Zipkin container for diagnostics and tracing.
- A default Dapr configuration and components installed in
$HOME/.dapr/(Mac/Linux) or%USERPROFILE%\.dapr\(Windows).
The dapr-placement service is responsible for managing the actor distribution scheme and key range settings. This service is not launched as a container and is only required if you are using Dapr actors. For more information on the actor Placement service read actor overview.
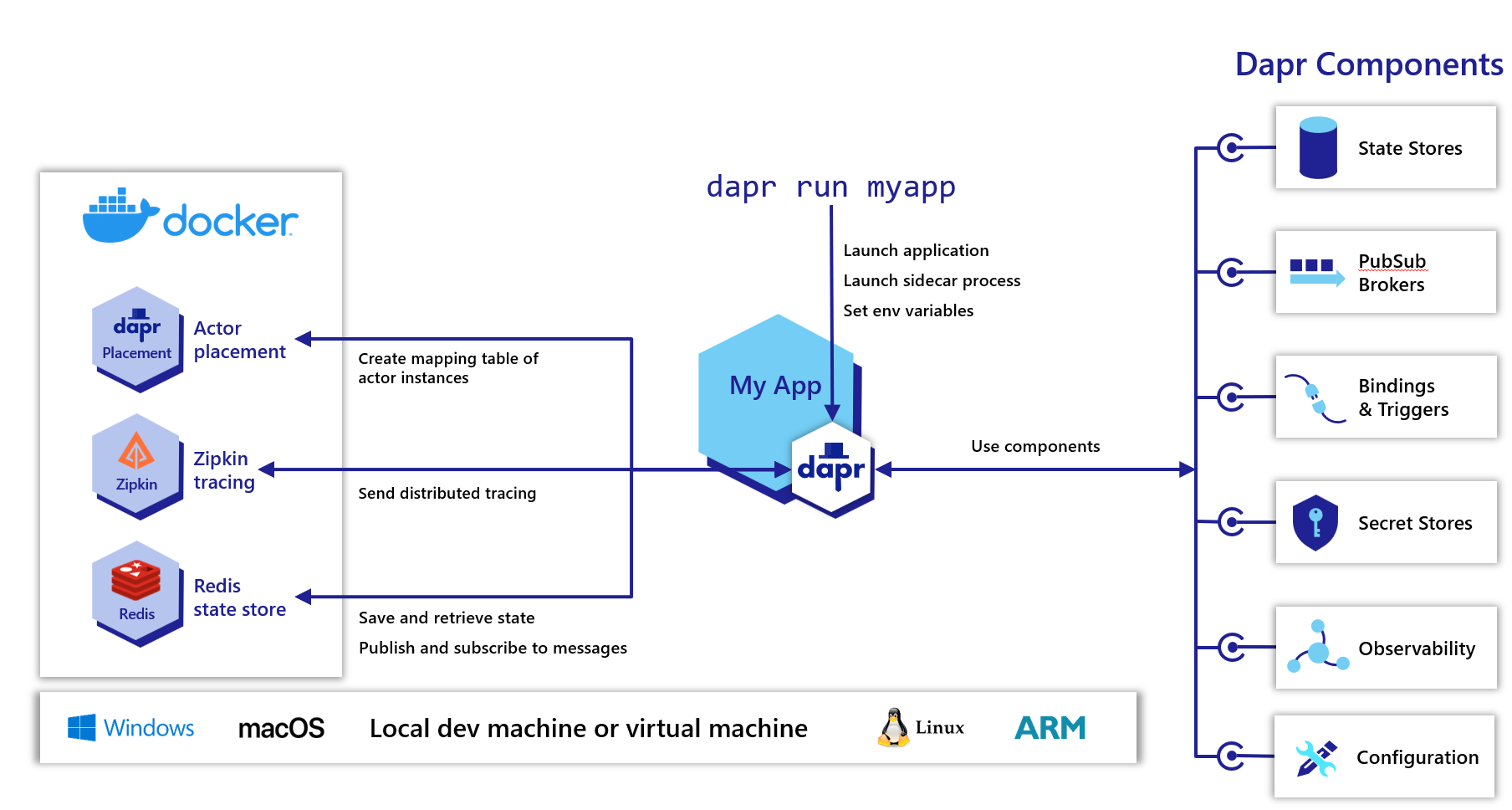
Launching applications with Dapr
You can use the dapr run CLI command to a Dapr sidecar process along with your application. Additional arguments and flags can be found here.
Name resolution
Dapr uses a name resolution component for service discovery within the service invocation building block. By default Dapr uses mDNS when in self-hosted mode.
If you are running Dapr on virtual machines or where mDNS is not available, then you can use the HashiCorp Consul component for name resolution.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Glad to hear it! Please tell us how we can improve.
Sorry to hear that. Please tell us how we can improve.